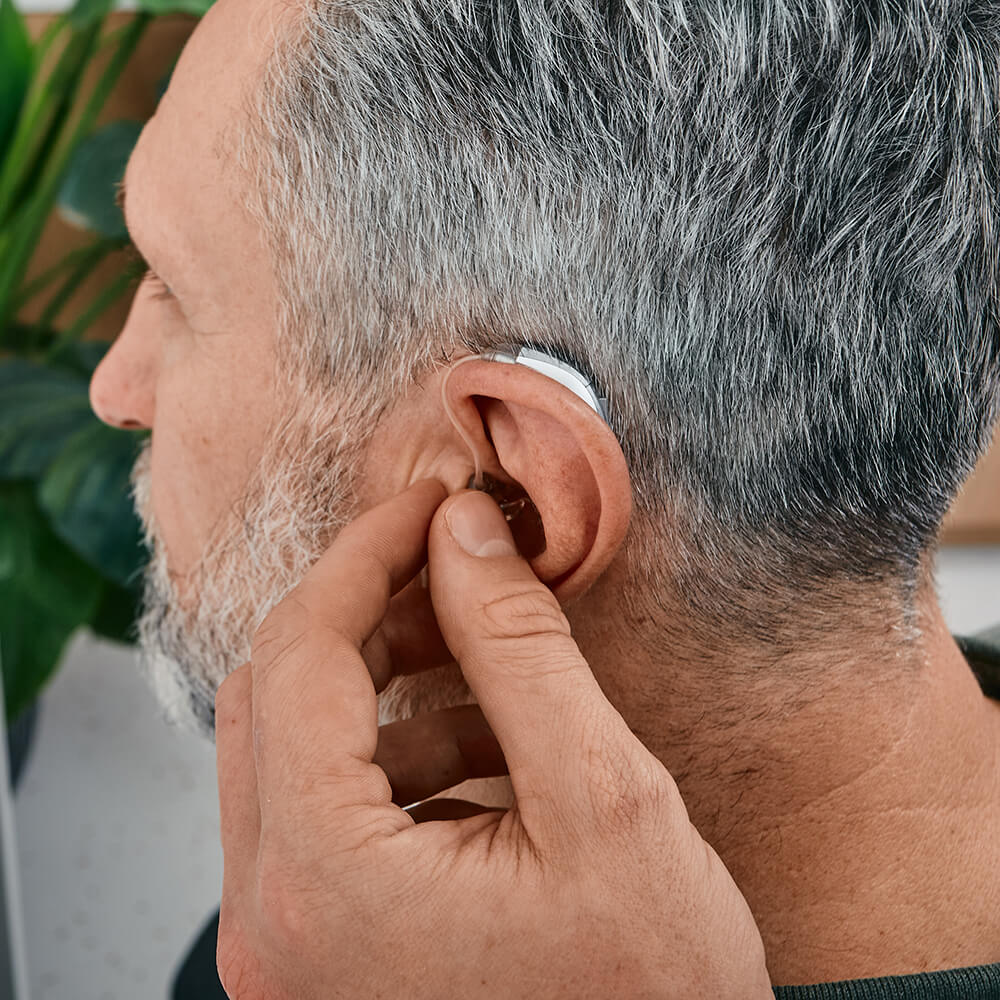
Hear What You’ve Been Missing!
Contact Us
Independently-Owned & Family-Operated
Our husband-and-wife team at Digital Hearing Lab proudly provides expert hearing services to our communities in Central Florida!
Learn More
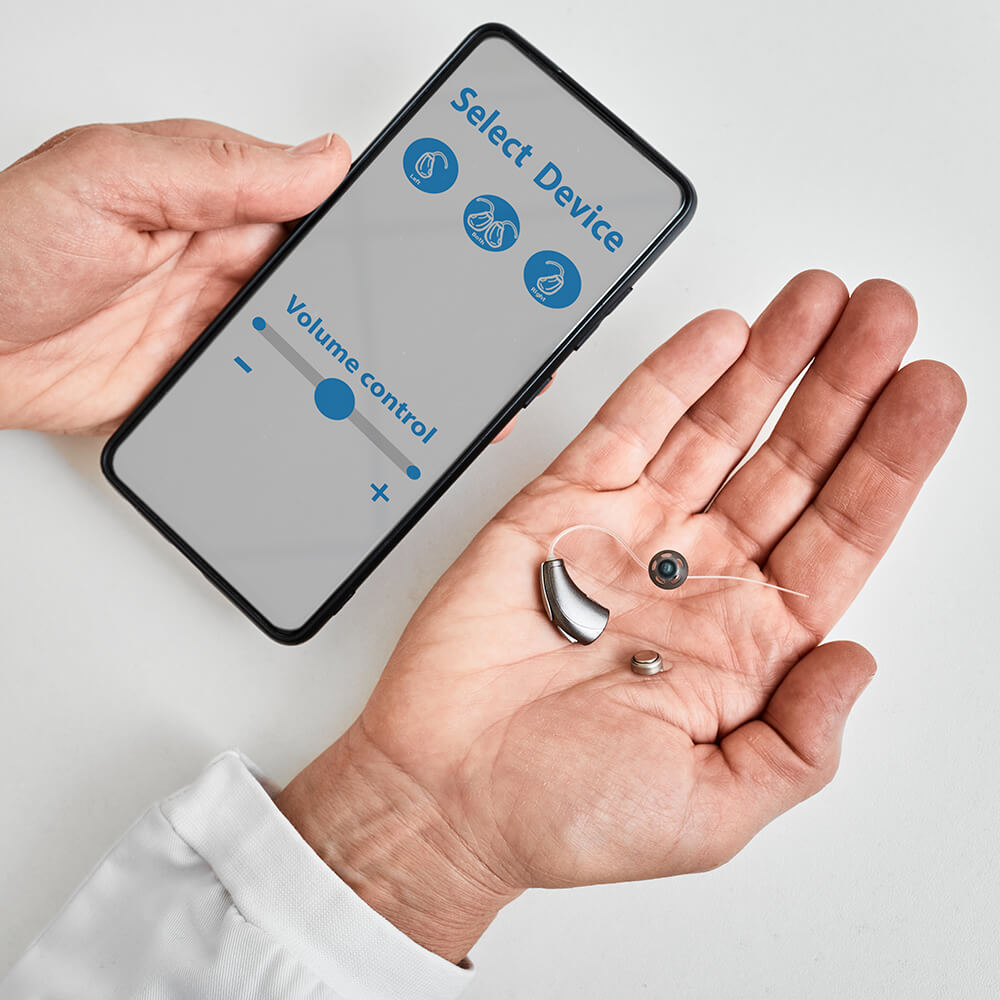
Hearing & Hearing Aids
From our precise and painless hearing test process to determining whether a hearing loss is present to pairing you with life-changing technology, we focus on your unique hearing needs.
Learn More
Tinnitus Therapy & Management
Tinnitus can be frustrating and debilitating. We understand that tinnitus can infringe upon many different areas of your life, and we know how challenging it can be to manage. Fortunately, we have solutions!
Learn More
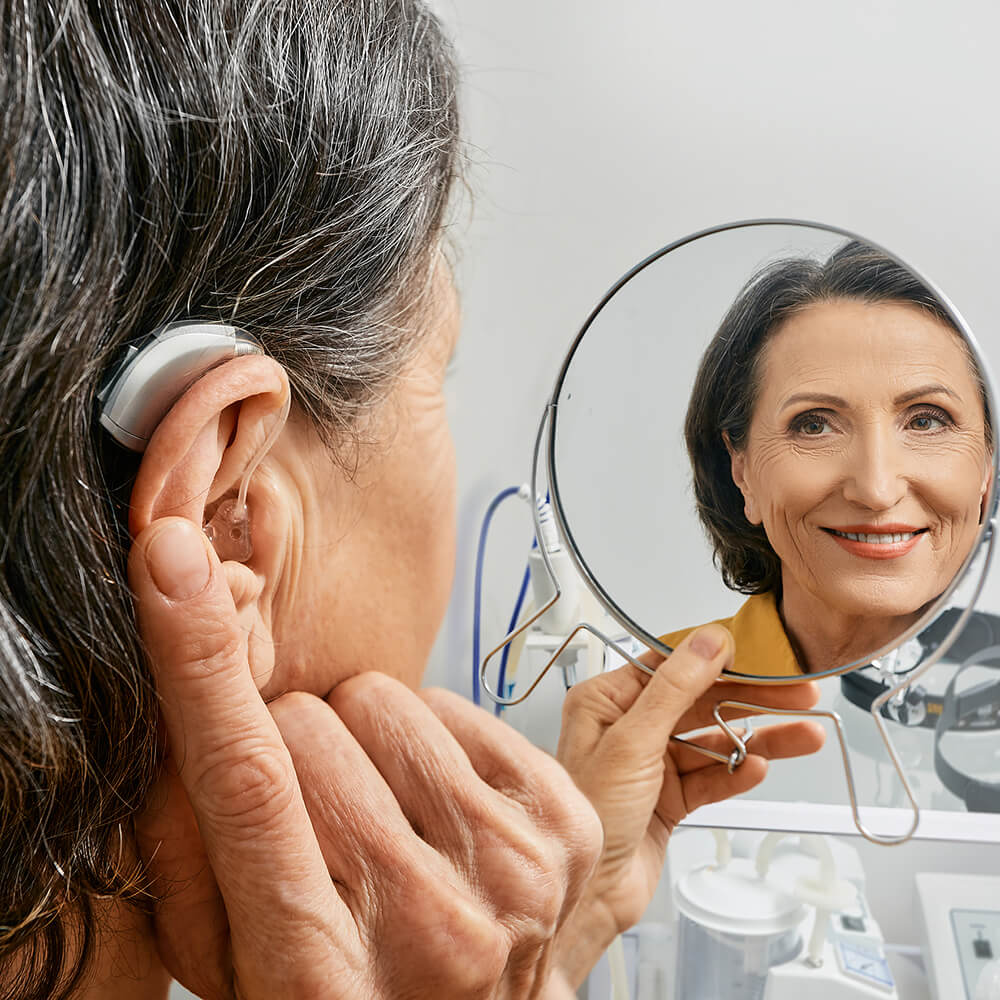

Welcome to Digital Hearing Lab Corp.
We are so happy you have found us! Digital Hearing Lab is an independent, family-owned, operated, full-service hearing practice by Gabriel Rodriguez and Stephanie Zang. We are proud Floridians based in Kissimmee, Clermont and Lady Lake, Florida, and we love our community. We are committed to providing our friends and neighbors with quality hearing services. We are excited to support you on your journey to better hearing.
Learn More
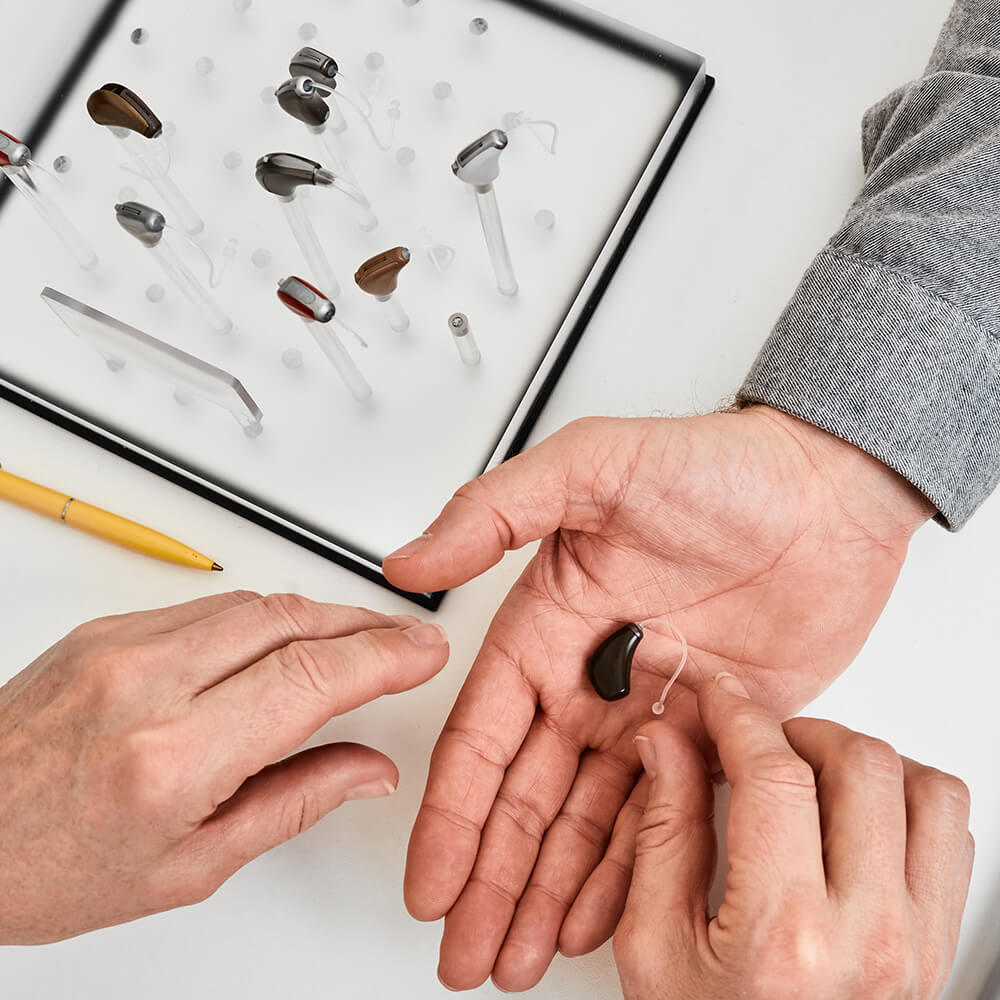

Why Choose Us
At Digital Hearing Lab, we understand the challenges of hearing loss and the joy of reconnecting to the sounds we’ve been missing. Our Kissimmee and Clermont roots help us connect to our patients and focus on the things that matter most. If you seek professional hearing services, look no further at Digital Hearing Lab!
- Family-owned & operated
- Personalized care and attention
- Commitment to centering your needs
- Expertise with the latest sophisticated hearing technology
- Community-focused, locally-based
- Providers fluent in Spanish, English, and German
- Professional hearing and tinnitus management services
Learn More
Manufacturers We Work With
Reconnect to the sounds of your life and hear what you’ve been missing!
Schedule an Appointment